SpesML Plugin - Data Types
SpesML Plugin - Data Types
Overview
Data types specify variables and channels. They define the range of values that can be assigned to a variable or messages that can be sent via a channel. A data type in SysML can be one of the following:
- Primitive types, which are values types predefined by SysML.
- Enumerations, defining a set of value literals
- Value types, which consist of several properties, each having a certain type and multiplicity
Primitive Types
The predefined primitive types are boolean, byte, short, char, int, long, float, and double.
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| boolean | Values are either true or false |
| byte | Values between -128 and 127 (8-bit signed integer) |
| short | Values between -32,767 and 32,767 (16-bit signed integer) |
| char | Values between \u0000 or 0 and \uffff or 65,535 (16-bit Unicode character) |
| int | Values between -2^{31} and 2^{31}-1 (32-bit signed integer) |
| long | Values between -2^{63} and 2^{63}-1 (64-bit signed integer) |
| float | Single precision floating point of the IEEE 754 standard (32-bit) |
| double | Double precision floating point of the IEEE 754 standard (64-bit) |
Enumerations
An enumeration is a data type representing a group of literals, i.e., constant values that can be assigned to variables and channels. Each enumeration must have a name and consists of one to many literals, wich also must have a name. In addition, enumerations may have a visibility (default is package).
Value Types
Value types combine primitive types, enumerations, and other value types to define more complex object structures. Each value type must have a name and optionally a visibility (default is package). A value type consists of one to many properties, which must have a name and type. A property may have a multiplicity (default is 1), whit possible multiplicities being 0, 1, 0..1, 1..*, and *.
The predefined value types are Integer, Real, String, and Boolean. The type Integer represents unbounded integer numbers, and the type Real represents the mathematical concepts of real numbers. String and Boolean are defined as usual.
How to Model
How to create Enumerations
The specify an enumeration with its literals, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to the
Data Typesfolder (or create it if it does not exist) -
Right-click on the folder and select Create Element. A dialog will open. Select Enumeration.
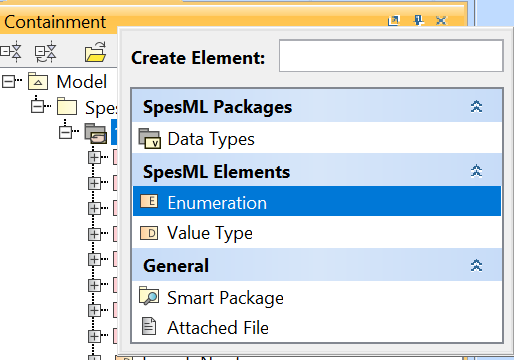
-
You are asked to choose a name for the enumeration:
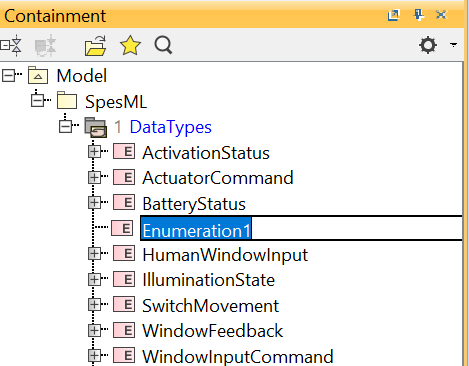
-
To add literals to the enumeration, right-click on the enumeration, select Create Element, and select Enumeration Literal
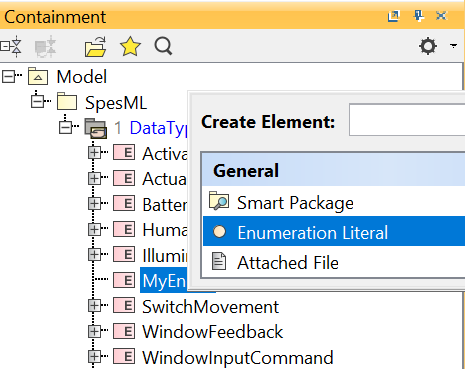
-
Give the created literals names.
How to create Value Types
The specify a value type with its properties, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to the
Data Typesfolder (or create it if it does not exist) -
Right-click on the folder and select Create Element. A dialog will open. Select Value Type.
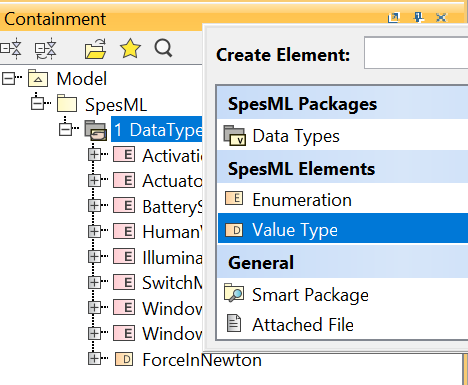
-
You are asked to choose a name for the value type:
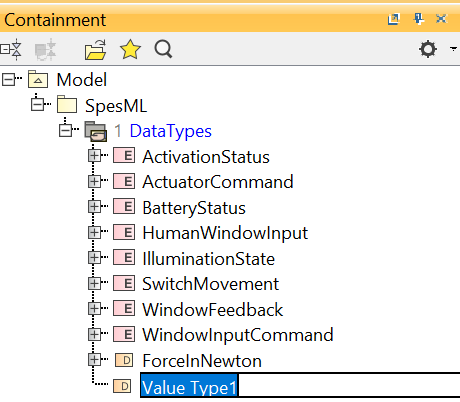
-
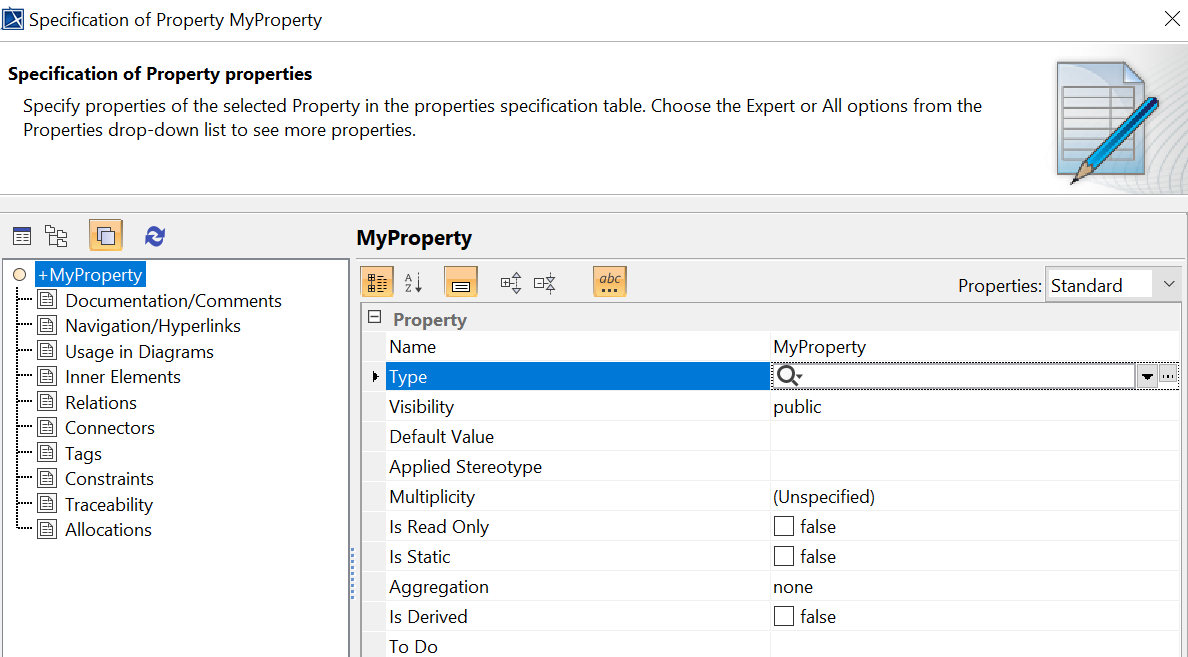
To add properties to the value-type, right-click on the value-type, select Create Element, and select Property
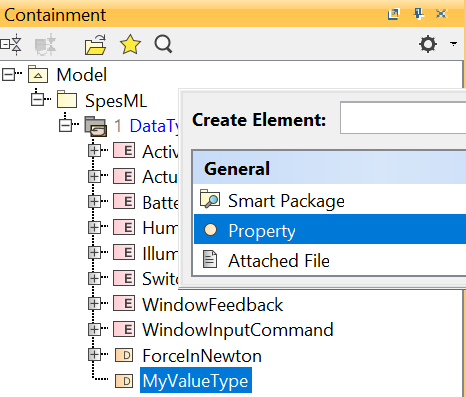
-
Give the created propertie a name.
-
To give the property a type, right-click on the property, select Specification. A window will open. Select a type in the field Type.