Views and Viewpoints
Multiple stakeholders with different concerns are typically involved in the engineering process of a software-intensive embedded system. The different stakeholders need different information in just as different presentations. The concept of viewpoints aims at separating the different concerns of stakeholders during the engineering process, so that every stakeholder can retrieve the information in the needed representation. Additionally, viewpoints serve as a construct for managing the different artifacts during the engineering process.
Viewpoint
The IEEE Standard 42010 characterizes viewpoints as a specification of the conventions for constructing and using a view. In other words, a viewpoint is a pattern, template or blueprint that can be used to develop individual views on a system (and its environment). Typically, the specification of a viewpoint defines its syntax, semantics and pragmatics by providing, among others:
- the name of the viewpoint,
- the corresponding stakeholder concerns,
- the viewpoint language,
- and techniques which can be used during the construction and analysis of the corresponding view.
View
Given a viewpoint specification, a view can be characterized as a concrete model of the system that represents the information that is relevant for the corresponding viewpoint concerns by using the conceptual structure of the underlying viewpoint language.
Views in the SPES Methodology
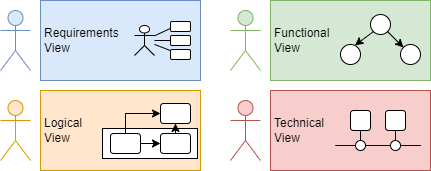
Figure 1 shows the four views that the SPES methodology provides by default:
- Requirements View for eliciting, documenting, negotiating, validating, and managing requirements for the system under development
- Funtional View for formalizing and transforming requirements into functional system specification
- Logical View for decomposing the system under development into an architecture of logical components in terms of a glass box view
- Technical View for holding the models of the platform dependant realization of the system and for breaking down the system into components that can be assigned to the various engineering disciplines.
Each of the different views is used by different stakeholders and contains just the information the stakeholder needs in the presentation suitable for the stakeholder.